Attenuates low frequencies below a selected cutoff, allowing higher frequencies to pass through.
This filter is commonly used to remove rumble, handling noise, or unwanted low-frequency energy while preserving clarity.
High Pass is a frequency-domain filter evaluated continuously over time.
Parameters
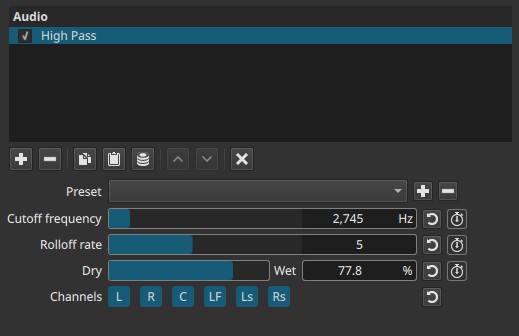
Cutoff frequency (5 - 21 600 Hz)
Defines the frequency below which audio is progressively attenuated.
-
Very low values (≈5 - 40 Hz)
Remove subsonic rumble without affecting audible content. -
Low values (≈60 - 120 Hz)
Clean up low-end noise while preserving most voice and music. -
Mid values (≈150 - 300 Hz)
Thin out sound deliberately; remove bass content. -
High values (>500 Hz)
Strong filtering effect; useful for special effects.
Intuition:
Raising the cutoff removes more bass.
Rolloff rate (1 - 10)
Controls how steeply frequencies below the cutoff are reduced.
-
Low values (1 - 3)
Gentle slope. Bass fades out smoothly. -
Mid values (4 - 7)
Clear cutoff with controlled transition. -
High values (8 - 10)
Aggressive filtering. Low frequencies are strongly suppressed.
Behavior note:
- Higher rolloff values can sound unnatural if set too high.
Dry → Wet (0.0 - 100.0%)
Controls the mix between the original signal and the filtered signal.
-
0.0%
Original audio only. -
50.0%
Balanced mix of filtered and unfiltered audio. -
100.0%
Fully filtered audio.
This allows subtle filtering without fully removing low frequencies.
Channel selection (toggle buttons)
Determines which audio channels the filter is applied to.
Buttons are toggle switches.
![]()
Available buttons depend on the project’s audio channel configuration; Settings / Audio Channels / 1, 2, 4, or 6 (channels)
- L — Front Left
- R — Front Right
- C — Center
- LF — Low-Frequency Effects (LFE)
- Ls — Surround Left
- Rs — Surround Right
Note:
Independent filtering per channel requires adding separate instances of the filter.
Auditory characteristics
- Reduced bass and low-frequency energy
- Improved clarity for dialogue
- Cleaner mixes with less rumble
- Excessive settings can make audio sound thin
Recommended use cases
- Dialogue cleanup
- Removing wind or handling noise
- Reducing low-frequency hum
- Preventing bass buildup in mixes
- Preparing audio before compression
Example settings
-
Dialogue cleanup
- Cutoff: 80 - 120 Hz
- Rolloff: 3 - 5
- Dry → Wet: 100%
-
Subtle rumble reduction
- Cutoff: 40 - 60 Hz
- Rolloff: 2 - 3
- Dry → Wet: 50 - 100%
-
Special effect (thin / radio-like sound)
- Cutoff: 300 - 600 Hz
- Rolloff: 6 - 8
- Dry → Wet: 100%
Usage notes and tips
- Start with the lowest effective cutoff.
- Increase rolloff only if low frequencies remain audible.
- For natural results, avoid extreme cutoff values.
- Always evaluate changes during playback.
Limitations
- Not a substitute for detailed equalization
- Cannot selectively remove specific bass notes
- Extreme settings can reduce audio naturalness